Introduction
What is a computer network?
A computer network is a system where multiple devices,such as computers,servers and other digital systems,are connected to share resources, information, and data. These connections enable seamless communication between devices,making collaboration and resource sharing more efficient. Networks have become a backbone of modern-day technology, allowing us to access the internet, share files, and connect to remote systems with ease.
Types of computer networks
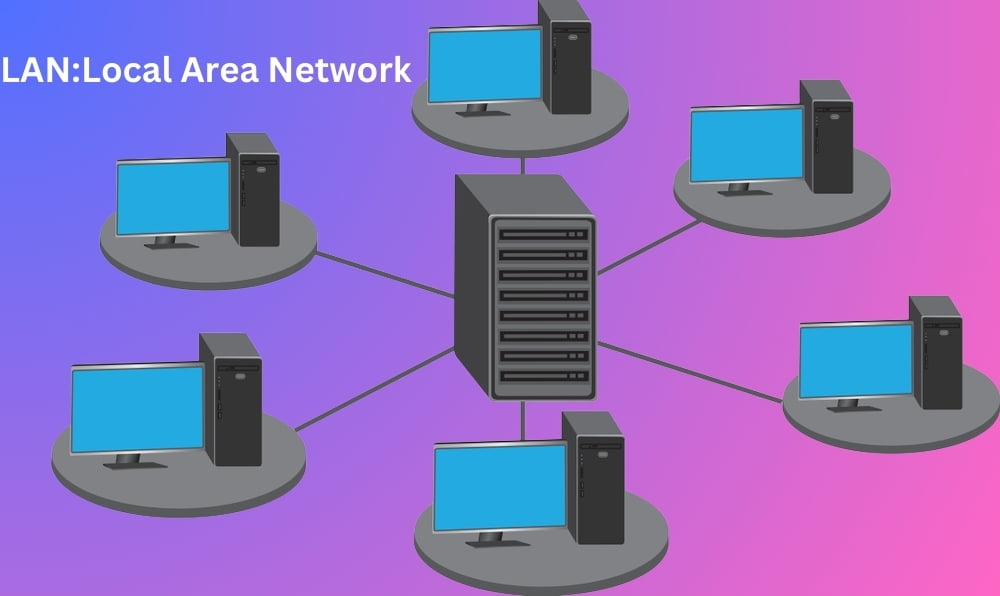
1.Local Area Network (LAN)
- A LAN is a computer network that covers only a small geographical area (usually within a square mile or less), such as an office, home or building. In a local area network, computers connected have a network operating system installed onto them.
- One computer is designated as the file server, which stores all the software that controls the network. It also stores the software that can be shared by the computers attached to the network. Other computers connected to the file server are called workstations.
- The workstations can be less powerful than the file server, and they may have additional software on their hard drives.On most LANs, cables are used to connect the computers.Generally, LAN offers a bandwidth of 10 to 100 Mbps.
- LANs are classified according to their data transfer speed, as: high speed, medium speed and low-speed LANs. In high-speed LANs data are transmitted at the rate a few gigabits per second (Mbps). Such LANs are designed to link server computers. In medium speed LANs data are transmitted at the rate of about a gigabits per second. Such LANs are suitable to link smaller servers and PCs. Example of a medium-speed LAN is Ethernet.Its speed is 1 Gbits/s. Low-speed LANs transmit data at a few hundred Mbps. They are suitable to link PCs and other workstations. Wireless LAN, called WLAN has also been developed.
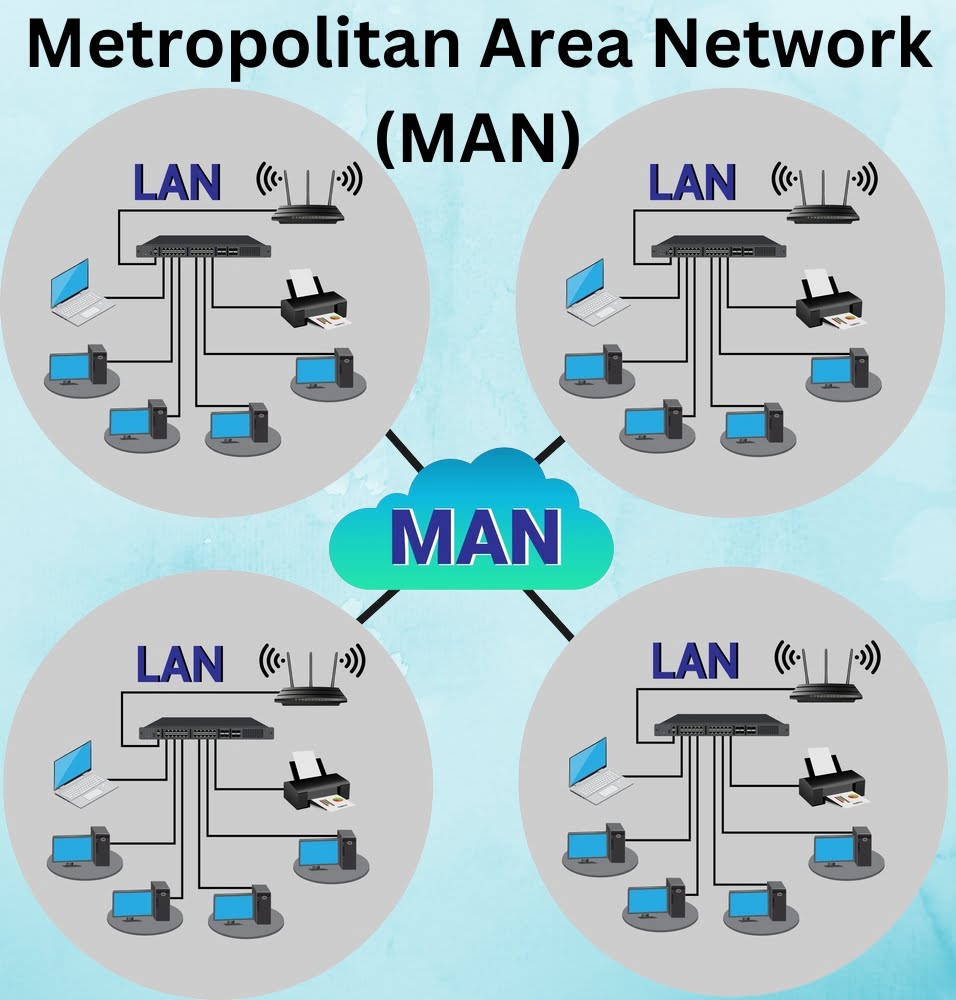
2.Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- A MAN, or Metropolitan Area Network, is a network of computers spread over a ‘metropolitan’ area such as a city and its suburbs. As the name suggests, this sort of network is usually reserved for metropolitan areas where the city bridges its local area networks with a series of backbones,making one large network for the entire city.
- It may be a single network such as a cable television network or it may be a means of
connecting a number of LANs. Note that MAN may be operated by one organization (a corporate with several offices in one city), or be shared resources used by several organizations in the same city.
3.Wide Area Network (WAN)
- A WAN, or Wide Area Network, is a system of interconnecting many computers over a large geographical area such as cities, states, countries or even the whole world. These kinds of networks use telephone lines, satellite links, and other long-range communications technologies to connect.
- Such networks are designed to serve an area of hundreds or thousands of miles such as public and private packet switching networks and national telephone networks. For example, a company with offices in New Delhi,Chennai, and Mumbai may connect the LANs for each of those locations to each other through a WAN.
- Although a WAN may be owned or rented by private business,it is usually a public network designed to connect small and intermediate sized networks together. The largest WAN in existence is the Internet.
WAN offers many advantages to business organizations. Some of them are as follows:
- It offers flexibility of location because not all the people using the same data have to work at the same site.
- Communication between branch offices can be improved using e-mail and file sharing.
- It facilitates a centralized company wide data backup system.
- Companies located in a number of small, interrelated offices can store files centrally and access each other’s information.
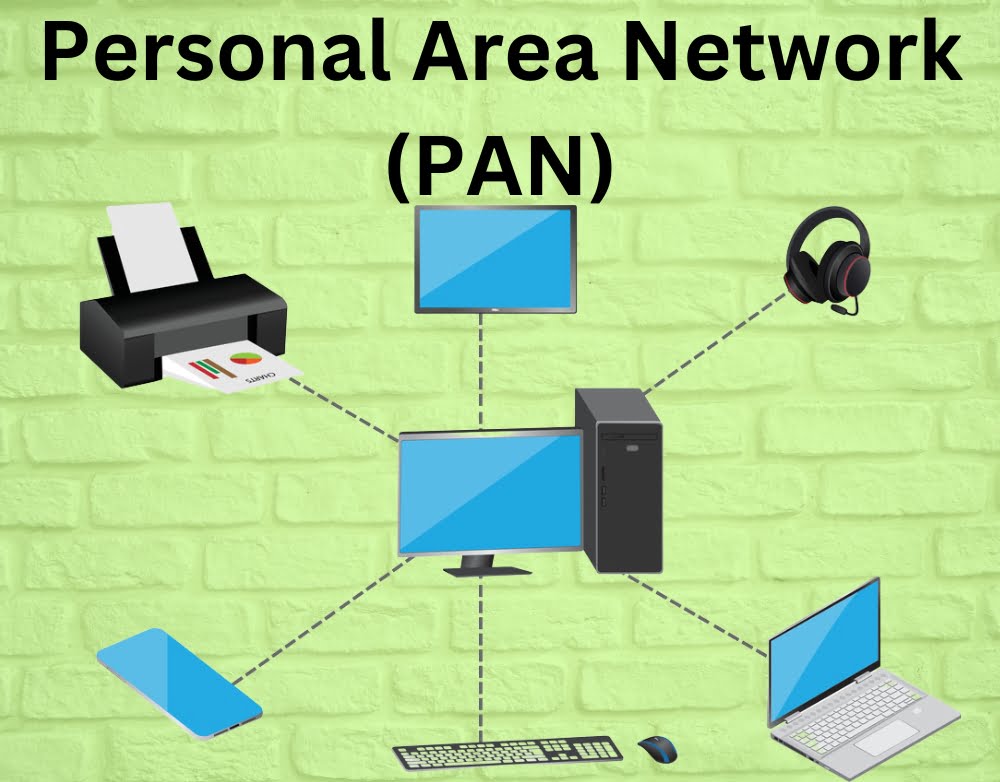
4.Personal Area Network (PAN)
- A Personal Area Network, known as PAN, is a compact network that links personal gadgets like smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices within a limited distance. Bluetooth and infrared are popular technologies that are frequently utilized for PANs to enable devices to exchange data and communicate within a restricted range, like a room or personal space.
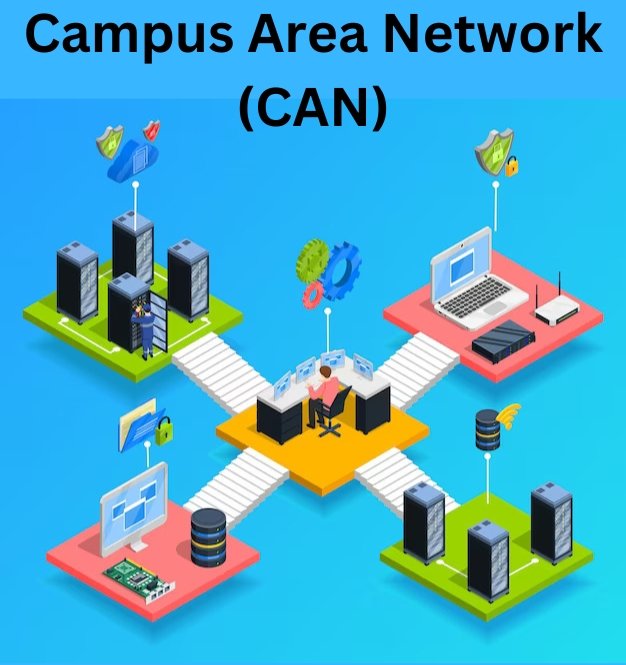
5.Campus Area Network (CAN)
- A Campus Area Network,known as CAN,links numerous LANs in a university campus,corporate campus or large organization.CANs enable communication and sharing of resources among various campus departments or buildings by utilizing high-speed fiber optic cables or wireless technologies.
6.Virtual Private Network
- A VPN, short for Virtual Private Network, is a protected network that enables individuals or branch locations to join a private network through the internet. VPNs utilize encryption and authentication protocols to guarantee secure communication and data privacy, which is perfect for remote work, telecommuting, and linking distributed networks.
Conclusion
Computer networks form the backbone of our interconnected world, enabling communication, data sharing, and resource access across vast distances. By understanding the different types of networks, we can better appreciate how these systems support everything from local file sharing to global internet access.