Introduction
Software plays a crucial role in the modern digital age, driving a wide range of systems from individual gadgets to elaborate corporate networks. Recognizing the different types of software is essential for efficiently moving through the extensive realm of technology. In this guide, we will explore the different kinds of software, including their features, instances, benefits, and uses in various industries.
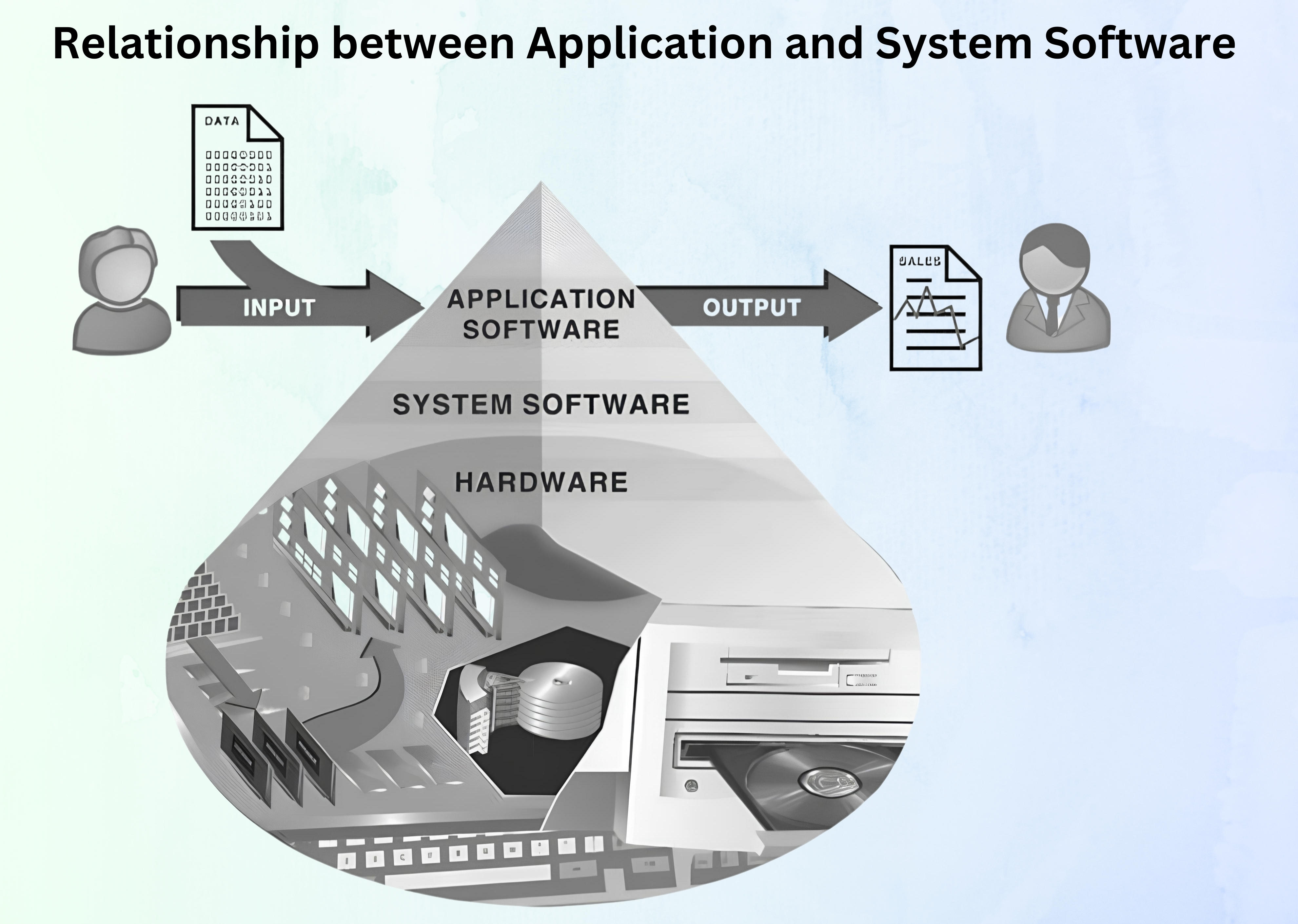
Software splits into two main types: system
software and application
software. System
software helps run the
computer, like a power plant generating electricity. Application
software uses the
computer to perform specific user tasks, like a bulb using electricity to provide light.
| Comparison Basis |
System Software |
Application Software |
| Definition |
Programs that control and manage computer hardware and system resources. |
Programs designed to perform specific tasks for users. |
| Purpose |
Provides a platform for application software and manages hardware. |
Applies computer power to solve real-world problems. |
| User Interaction |
Mostly works in the background and is less visible. |
Directly interacts with users. |
| Dependency |
Independent of application software. |
Depends on system software to function. |
| Examples |
Operating systems, device drivers, language translators, system utilities. |
Word processors, spreadsheets, image editors, database systems. |
1. System Software
| Aspect |
Description |
| Control |
Controls and manages computer hardware. |
| Installation |
Usually pre-installed by the manufacturer. |
| Programming Support |
Provides an environment for developers to create applications. |
| Interface Role |
Acts as an interface between hardware and application software. |
| Core Features |
File management, display handling, keyboard input, system resource control. |
1. Operating System
| Feature |
Description |
| Startup Function |
Loads first into memory when the computer starts. |
| Core Services |
Provides disk access, memory management, task scheduling, and user interface services. |
| Program Coordination |
Ensures programs running simultaneously do not interfere with each other. |
| Main Role |
Organizes and controls hardware resources. |
| Examples |
Windows XP, UNIX, Linux. |
| Operating System Function |
Description |
| Process Management |
Handles creation, deletion, suspension, resumption, and synchronization of processes. |
| Memory Management |
Allocates and de-allocates memory space as required by programs. |
| File Management |
Creates, stores, retrieves, organizes, and protects files and directories. |
| Device Management |
Manages devices such as printers and modems and detects failures. |
| Security Management |
Protects system resources from unauthorized access and destruction. |
| User Interface |
Provides communication between the user and hardware. |
2. Device Drivers
| Aspect |
Description |
| Definition |
System programs that enable hardware devices to function correctly. |
| Requirement |
Each hardware device requires its own specific driver. |
| Function |
Translates operating system commands into device-specific instructions. |
| Examples |
Printer driver, monitor driver, keyboard driver, mouse driver. |
3. Language Translators
| Translator Type |
Description |
| Compiler |
Converts entire high-level programs into machine code before execution. |
| Interpreter |
Translates and executes source code line by line. |
| Assembler |
Converts assembly language into machine code for execution. |
| Additional System Programs |
Description |
| Linker |
Merges multiple object modules and libraries into a single executable program. |
| Loader |
Loads the executable program into memory and manages its execution. |
4. System Utility
| Utility Function |
Description |
| File Management |
Finds, organizes, copies, moves, and deletes files and directories. |
| Backup |
Creates copies of data to prevent data loss. |
| Data Recovery |
Retrieves deleted or inaccessible data from storage devices. |
| Virus Protection |
Protects the system from malicious software and removes threats. |
| Disk Management |
Includes disk defragmentation, compression, and formatting tools. |
| Firewall |
Prevents unauthorized network access. |
| Disk Cleanup |
Removes unnecessary files to improve system performance. |
2. Application Software
| Aspect |
Description |
| Purpose |
Used to accomplish specific tasks for users. |
| Dependency |
Relies on system software to operate. |
| Structure |
Can be a single program, software package, or software suite. |
| Practical Role |
Applies computer processing power to business and personal tasks. |
Figure 1
Types of Application Software
| Application Type |
Description |
Examples |
| Word Processors |
Create, edit, format, and print electronic documents. |
Microsoft Word, WordPerfect |
| Spreadsheets |
Perform calculations and manage financial records using grid-based cells. |
Microsoft Excel, Lotus 1-2-3 |
| Image Editors |
Create, edit, and manipulate digital images. |
Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW |
| Database Management Systems |
Store, retrieve, organize, and manage structured data efficiently. |
FoxPro, Oracle |
| Presentation Applications |
Create slide-based visual presentations. |
Microsoft PowerPoint |
| Desktop Publishing Software |
Design magazines, books, newsletters, and other printed documents. |
QuarkXPress, Adobe PageMaker |
Conclusion
System software and application software play essential roles in the digital environment, with each fulfilling specific functions to support computer operations and enhance user interaction. It is crucial for users, developers, and IT professionals to comprehend the distinctions between these categories and investigate different types within them in order to fully utilize the power of software in today's technology-driven society.