Introduction
In the vast tapestry of communication, where ideas, information, and emotions intertwine, digital communication stands as a transformative force. This method of conveying messages, born from the marriage of technology and data, has become the cornerstone of our interconnected world. In this exploration, we dissect the essence of digital communication, understanding its principles, modes, and the profound impact it has on how we connect and share.
A significant point about communication is that it involves a sender (transmitter) and a receiver. Only the receiver completes the communication process. You can define communication as the dual process of “transmitting and receiving” or “coding and decoding” information, making it a two-way process.
Defining Digital Communication
COMMUNICATION
- Communication is the science and practice of transmitting information.
- Communication Engineering deals with the techniques of transmitting information.
- In brief, Communication Engineering means Electrical Communication, in which information is transmitted through electrical signals.
- Electrical Communication is a process by which the information/message is transmitted from one point to another, from one person to another, or from one place to another in the form of electrical signals, through some communication link.
- Message or information
- Sender, transmitter or coder
- Receiver or decoder
- Code
- Channel (transmission path)
METHODS OF COMMUNICATION
The communication may be:
Principles of Digital Communication
1. Digitalization:
2. Encoding:
3. Modulation:
4. Error Detection and Correction:
PROCESS OF COMMUNICATION
4.Decoding: The coded message is decoded into the original form, so that it is easily understood by the person on the receiver side.
information for the purpose, it has been transmitted.
BRIEF HISTORY OF COMMUNICATION
ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION
STRUCTURE OF AN ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION
SYSTEM
2.Transmitter
3.Receiver
- The information source: The information source is the source which generates or produces information or signal.
- Transmitter: Transmitter is the device which transmits the generated information or signal. It has the following components:
1.Coding:The transformation of the signal into a suitable form in which it can be transmitted.
2.Modulation:To superimpose the signal on an H.F. carrier, so that the signal can travel long distances.
- Receiver: It receives the information, e.g., radio receiver, T. V. receiver,telephone receiver, etc. It consists of:
1.Decoding: It is the reverse of coding, e.g., to regain the original form of the signal.
2.Demodulation: It is the reverse of modulation, i.e., to separate the original signal from the carrier.
Modern Communication System Scheme
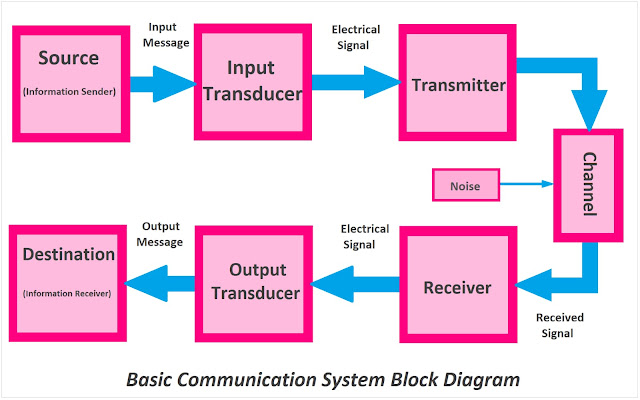
- A basic communication system provides a link between the information source and its destination.
- The process of electrical communication involves sending,receiving, and processing information in electrical form.
- The information you want to transmit passes through several stages in the communication system before it reaches its destination.
- Fig. 2 shows a block schematic diagram of the most general form of basic communication system.
- The main constituents of basic communication system are:
1.Information source and input transducer
2.Transmitter
3.Channel or medium
4.Noise
5.Receiver
6.Output transducer and final destination
Information Source and Input Transducer
- A communication system transmits information from an information source to a destination.
- Hence the first stage of a communication system is the information source.
- A communication system transmits information in the form of electrical signals.
- If the information produced by the source is not in an electrical form, one will have to use a transducer to convert the information into electrical form.
- A transducer is a device that converts a non-electrical energy into its corresponding electrical energy called signal and vice versa.
- An example of a transducer is a microphone.Microphone converts sound signals into the corresponding electrical signals.
- Similarly, a television (TV) picture tube converts electrical signals into its corresponding pictures.
- Some other examples of transducers are movie cameras, Video Cassette Recorder (VCR) heads, tape recorder heads, and loudspeakers.
- The information source produces information, and you apply it to the next stage, called the information or input transducer.
- This in turn, produces an electrical signal corresponding to the information as output.
- You call this electrical signal the baseband signal. You also refer to it as a message signal, information signal, intelligent signal, or envelope.
- In communication theory, you usually designate the baseband signal as 𝑠(𝑡).
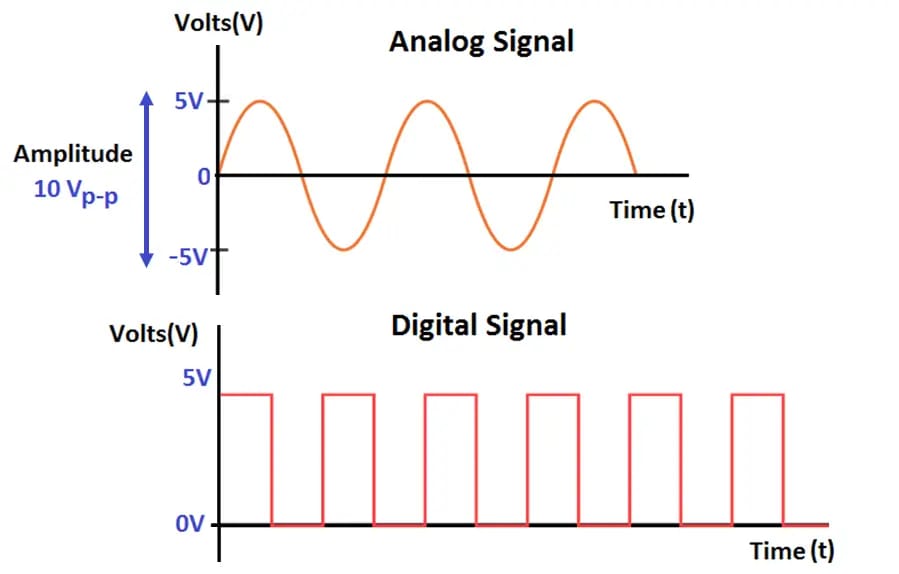
There are two types of signals:
2.Digital signal
1.Analog signal
- An analog signal is a function of time,and has a continuous range of values.
- However, there is a definite function value of the analog signal at each point of time.
- Examples: a pure sine wave form, a voice signal.
2.Digital signal
- A digital signal does not have continuous function values on a time scale.
- It is discrete in nature, i.e., it has some values at discrete timings.
- In between two consecutive values, the signal values is either zero, or different value.
- Example: the sound signal produced by drumbeats.
- Digital signals correspond to a binary digital signal, where you code the signal’s discrete amplitude into binary digits represented by ‘0’ and ‘1’.
- You convert the analog signal to digital using Analog to Digital Converters (ADC).
- ADC involves Sampling and Quantization.
- Sampling – converts analog time to discrete time
- Quantization – converts analog amplitude to discrete amplitude
Modes of Digital Communication
1. Point-to-Point Communication
Point-to point model involves passing of information from one entity to another. All this may involve anything from simple acts such as mailing determined writing to extremely intricate communication between devices in a network.
2. Broadcast Communication
A means of broadcasting is the transmission between a sender to several reception units. The classical examples include television and radio broadcasting while the modern digital includes streaming or online contented delivery.
3. Multipoint Communication
Multipoint communication facilitates concurrent interaction of multiple entities. Multipoint communication is observable in the form of video conferencing, online meetings and collaborative platforms on digital landscape.
Digital Communication Technologies
1. Internet Communication
The internet – the global system of interconnected computers, is a huge reservoir of digital communication. Major instruments of Internet communication include transatlantic mail email, instant messaging social media and video conferencing.
2. Mobile Communication
The range of Mobile Communication is huge as communication over mobile just does not refer only to voice calls but it covers all the functionality like texting, mobile internet and also app based communications. Connectivity advances with mobile technologies like 4G and the latest generations. Although newer generations continue to develop, many regions have not fully implemented them yet, making connectivity uneven.
3. Wireless Communication
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, firstly, belong to wireless technology, secondly, enabling devices to communicate without cables. Moreover, in addition, furthermore, also, besides, likewise, similarly, as well as, additionally, specifically, in particular, notably, to illustrate, for example, for instance, indeed, in fact, thus, therefore, consequently, as a result, hence, nevertheless, and ultimately, these technologies are essential for smart device interconnection.
Digital Communication – Its Effect
1. Global Connectivity
Digital communication firstly erased geographical barriers. Secondly, the web became an inexhaustible marketplace of thoughts and data. Moreover, in addition, furthermore, also, besides, likewise, similarly, as well as, additionally, specifically, in particular, notably, to illustrate, for example, for instance, indeed, in fact, thus, therefore, consequently, as a result, hence, nevertheless, and ultimately, digital communication continues transforming global information sharing.
2. Efficiency and Accessibility
The fast-paced nature of digital communication makes it efficient. Firstly, data is, indeed, just an eye-click away, secondly, allowing us to work even in real time. Moreover, in addition, furthermore, also, besides, likewise, similarly, as well as, additionally, specifically, in particular, notably, to illustrate, for example, for instance, thus, therefore, consequently, as a result, hence, nevertheless, and ultimately, collaboration facilities are available everywhere, accessible through various optic networks and the web.
3. Transformation of Industries
Digitized communication has transformed industries from medicine to education. Firstly, examples include telemedicine, secondly, online education, thirdly, and e-commerce. Moreover, in addition, furthermore, also, besides, likewise, similarly, as well as, additionally, specifically, in particular, notably, to illustrate, for example, for instance, indeed, in fact, thus, therefore, consequently, as a result, hence, and ultimately, digitized communication continues reshaping industries.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Security and Privacy
The online world raises serious concerns about information security and privacy. Firstly, securing user information and privacy are key issues in cybersecurity. Moreover, in addition, furthermore, also, besides, likewise, similarly, as well as, additionally, specifically, in particular, notably, to illustrate, for example, for instance, indeed, in fact, thus, therefore, consequently, as a result, hence, nevertheless, and ultimately, protecting user data remains a top priority.
2. Digital Divide
Even though people everywhere embrace and enjoy digital communication, a gap still exists between those who have technology and can connect online and those who cannot. Closing this gap is necessary to ensure equal opportunities and participation in the digital age.