Introduction
An ignition system of an internal combustion engine is a key element that triggers the ignition of a precisely measured air-fuel mixture within a combustion chamber to initiate the combusting process. Such fuel has a great impact on starting and running the engine smoothly. Here, we will examine the ignition system in great detail, cover its functions, constructs and different types.
Functions of the Ignition System
- Ignition Timing: Spark ignition system produces the spark at the right time during the compression stroke to achieve concerted yet efficient power output.
- Starting the Engine: The engine is started by the ignition system using a certain kind of spark to ignite the start of the combustion.
- Engine Performance: A good ignition system makes the engine work well, and when fuel is burnt, it is done evenly, and there is even power delivered.
- Emissions Control: Proper ignition timing has function of emissions control, because it guarantees full burn of air-fuel mixture.
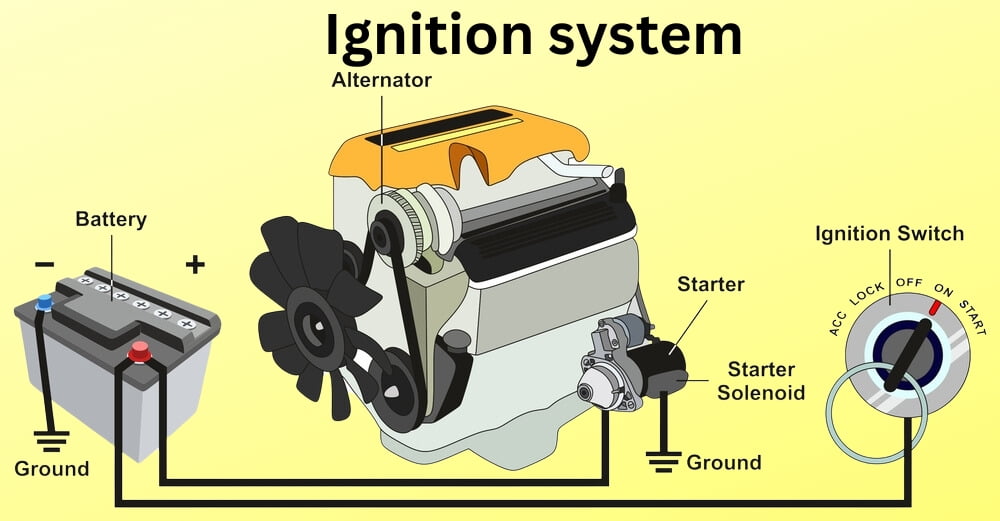
Components of the Ignition System
- Battery: Electrical energy needed to startup the ignition.
- Ignition Switch: Regulates the arrival of electric impulse to the ignition system.
- Ignition Coil: Converts the released low-voltage from the battery into high-voltage pulses, which power the spark plugs.
- Distributor (in older systems): Submits the high voltage electricity to the spark plugs in its correct engine order.
- Spark Plugs: Build a spark to catalyze the air-fuel mixture combination in the chamber dedicated for combustion.
- Ignition Control Module (ICM): Logically, it controls the timing and the duration of the spark for each spark plug.Ignition Timing Sensor detects the spark plug's position in order to precisely time the engine ignition.
Different Types of Ignition Systems
1. Conventional (Mechanical) Ignition System
- The regular ignition system which is also called a mechanical ignition system used to be common in older cars. It uses mechanical parts like the points and the distributor to time the spark.
- Key features include Point that is Contacts that mechanically open and shut to control electric flow to the ignition coil.
- Distributor that Extends high-voltage electricity from the ignition coil to each spark plug in the right order.Simple in design, easy to maintain. Increased wear and tear, less precise timing control.
2. Electronic Ignition System
Modern vehicles come in ignition systems which are electronic instead of using mechanical ones for reasons such as more durable and efficient performance.
- Ignition Control Module (ICM): It automatically provides the required ignition time and duration regulation.
- Hall Effect Sensor or Crankshaft Position Sensor: Total monitoring of the engine position for perfects sensor mimics. Higher initial cost, requirement of specialized diagnostic tools to detect errors is also important.
3. Distributorless Ignition System (DIS)
Distributor-less ignition systems have no distributor which was used earlier in old systems and replacing them with individual ignition coil for every spark plug.
- Individual Ignition Coils: On each spark plug, there is a coil that is managed by the electric system.
- Engine Control Module (ECM): Is in charge of spark ignition and distributes to individual ignition coils. The higher efficiency, the more precise and no much maintenance. Sophisticated wiring, the risk of an ignition coil abuse.
4. Cop Ignition Type
Spark plugs having the concept of Coil-on-Plug DIS type bring about one level higher of ignition system setup by locating the coils directly on each spark plug.
- Ignition Coils Mounted on Spark Plugs: The wires of high voltage and the losses of electricity are eliminated.
- Integrated Electronics: The coil includes built-in electronics for timing and thus voltages are properly maintained. Rise in individual coil cost and possible warming of the coil.
5.Spark Ignition system
A spark ignition engine is an engine that burns gasoline or those that run on gas. The electrical input needed to obtain a spark in the spark plug can be source from the battery or a magneto.
6.Compression Ignition system
Compression ignition engines are diesel engines in which air is highly compressed to raise its temperature and initiate combustion when diesel fuel is injected.
Conclusion
The ignition system plays a vital role in how the engine functions, as it starts the engine and ensures it performs at its best. Advancements in ignition technology, from traditional mechanical systems to modern electronic and coil-on-plug designs, have enhanced the reliability, efficiency, and emissions control in vehicles. Having knowledge of the various kinds of ignition systems allows car enthusiasts, mechanics, and engineers to understand the development and intricacy of engine ignition technology.