Introduction
Smart material are those materials which exhibit considerable changes in their mechanical properties like strain (Deformation) and viscosity, when subjected to changes in thermal, electrical or magnetic field changes. These properties can be exploited to develop sensors and devices which can respond to changes automatically. Hence such materials are called as intelligent/active/adaptive materials also.
What is smart materials?
These are the materials which exhibit considerable changes in their mechanical properties like strain (Deformation) and viscosity, when subjected to changes in thermal, electrical or magnetic field changes. These properties can be exploited to develop sensors and devices which can respond to changes automatically. Hence such materials are called as intelligent/active/adaptive materials also. Currently available smart materials are:
- Shape Memory Alloy (SMA)
- Magnetostrictive Materials
- Piezoelectric Materials
- Electrostrictive Materials and
- Electro-rheological Fluids.
Shape Memory Alloy (SMA)
These are the metallic materials which demonstrate the ability to return to some previously defined shape or size when subjected to appropriate thermal change. Materials that exhibit shape memory only upon heating are referred to as having one way shape memory. Some materials undergo a change in shape upon cooling also. These materials are said to have two way shape memory.
There are wide variety of alloys which exhibit shape memory. However for commercial exploitation only Niti (Nickel alloys) and the copper base alloys such as CuZn Al (Copper-Zinc-Aluminium) alloys are found useful.
Niti alloys have greater shape memory (up to 8%) compared to copper base alloys (4-5%). The Niti alloys are thermally stable and have excellent corrosion resistance also. Copper based alloys have medium corrosion resistance and susceptive to stress corrosion cracking. However the advantage of copper based alloys is that they are cheap and they can be melted and intruded with ease.
Magnetostrictive Materials
These materials undergo deformation when subjected to magnetic field. Most ferromagnetic materials exhibit some measurable magnetostriction. The higher known magnetostriction are those of iron alloys containing rare earth elements Dysposium (Dy Fe2) or Terbium (TbFe2).
Piezoelectric Materials
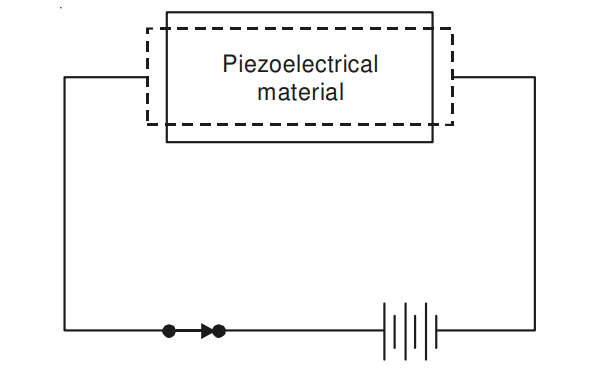
Piezoelectrical materials are the most widely used smart materials. These materials undergo surface elongation when an electrical field is applied across them and produce voltage when surface strain is introduced. Figure 1 and 2 show these phenomenon. The materials which exhibit piezoelectrical property are non-metallic materials such as quartz, Rochelle salt. Polyvinylidene fluid (PVDF), which can be easily formed into very thin sheet (film) and adhered to any surface is very commonly used smart material.

Figure 2
Electrostrictive Materials
- Electrostrictive materials are similar to piezoelectric materials in that both are ferroelectric crystals, exhibit a dimensional change upon an applied electric field or an electric polarization upon an applied mechanical stress.These materials are identical to piezoelectric materials, with better strain capacity but very sensitive to temperature.
- However, the electrostrictive actuators use a lead-magnesium-niobate (PMN) crystal stack while piezoelectric actuators use lead-zirconate-titanate (PZT) based ceramics.
- Unlike piezoelectric devices, PMN ceramics are not poled.
Electrorheological Fluids
Electrorheological fluids are colloidal suspensions that exhibit reversible change in viscosity when subjected to an electric field. The property of electrorheological fluids of reversible transition from liquid to solid state has been utilised in many engineering applications. These changes could be reversed in time intervals of the order of milliseconds.
Applications
- Aircrafts and space crafts are large structures which have to float in air. Hence they should be as light as possible. When weight reduction is made from the consideration of only primary forces, the problem of structural instability, excessive deflection and excessive vibration result. The sensors and actuators are used to dampen the vibration and to reduce deflections. They are fixed at optimum positions to control vibrations. The instabilities are sensed using sensors made of smart materials. Signals are processed in computers and corrective forces are developed through actuators which are made of smart materials.Below Figure shows the method of building a structure (plate or beam) so that they can sense and react to lateral instability.

2. Smart concrete is obtained by reinforcing the concrete with carbon fibres as much as 0.2% to 0.5% of volume of concrete. Carbon fibres increase the electrical resistance to deformation. Strain is detected through measurement of electrical resistance. Hence warning system can be developed to detect flaws in concrete structure following the changes in intercondition following an earthquake. This method of producing smart material is cheaper than the method of attaching or embedding the sensors and actuators.
3. By providing highway with smart concrete it is possible to find the weight and speed of vehicle moving on it.
4. Smart concrete is used to dampen vibration or reduce earthquake damage.
5. Smart concrete is useful in studying soundness of bridge structures.
6. Electrorheological fluids are used in clutches, values and engines.
7. Smart materials are used to develop safety, security and emergency control systems in buildings and cars.
8. Smart windows having impact on heating, ventilation and air conditioning loads are developed for use in buildings and automobiles.
Conclusion
The use of smart materials revolutionizes civil structure design and construction, improving performance and sustainability by boosting energy efficiency and reducing maintenance requirements. With technological advancements, smart materials are expected to play a larger role in civil engineering, leading to more innovative and durable infrastructure.